
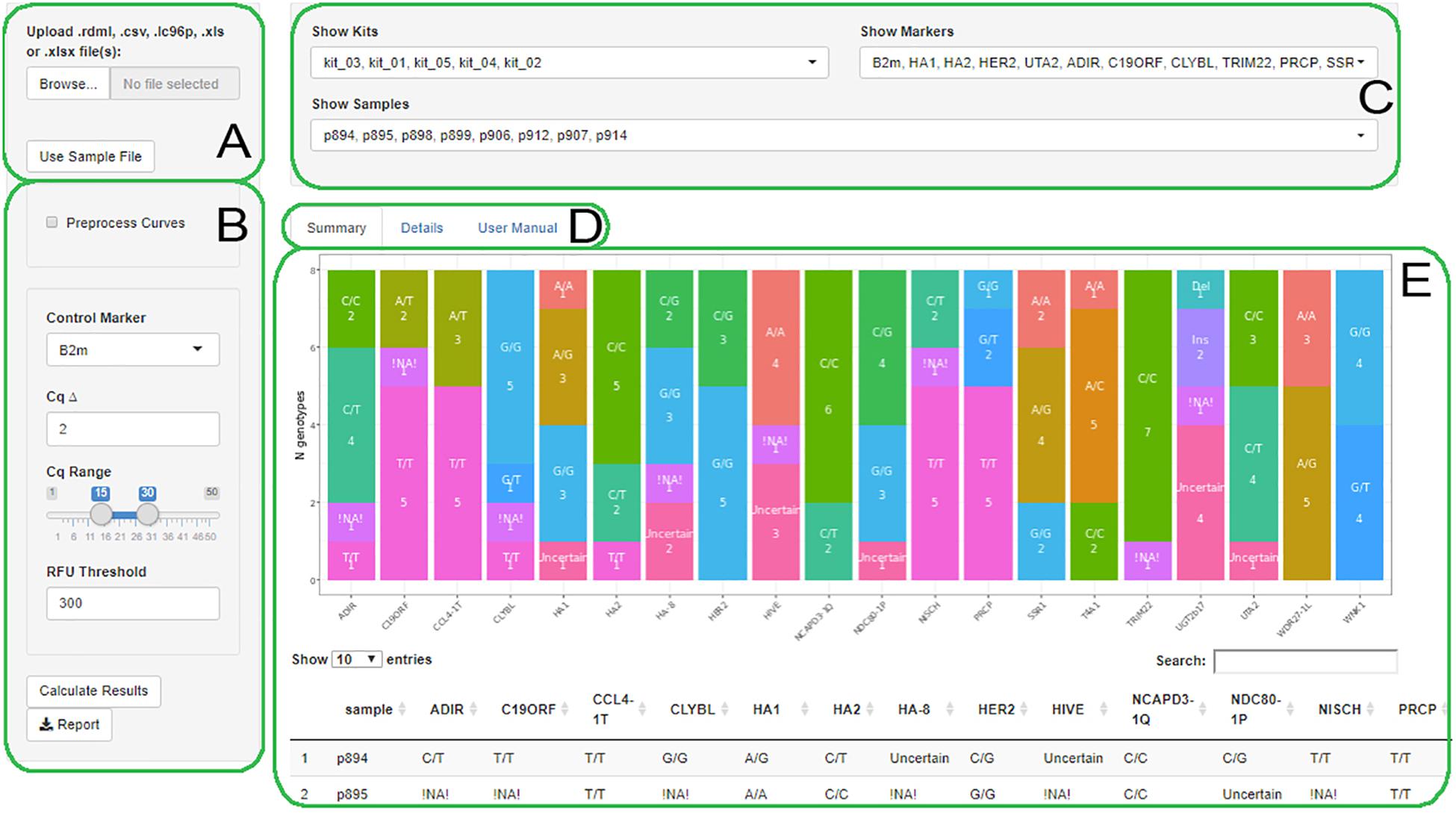
In this circumstance, both target efficiency (E target) and control efficiency (E control) equals 2, indicating amplicon doubling during each cycle, then there would be the same expression ratio derived from 2 -ΔΔCt. The ΔΔCt model can be derived from the efficiency-calibrated model, if both target and reference genes reach their highest PCR amplification efficiency. As shown in Equation 1, the ratio of target gene expression in treatment versus control can be derived from the ratio between target gene efficiency (E target) to the power of target ΔCt (ΔCt target) and reference gene efficiency (E reference) to the power of reference ΔCt (ΔCt reference). ΔCt for each gene (target or reference) is then calculated by subtracting the Ct number of target sample from that of control sample. Ct number is first plotted against cDNA input (or logarithm cDNA input), and the slope of the plot is calculated to determine the amplification efficiency (E). The efficiency-calibrated model is a more generalized ΔΔCt model.
Unless specified as percentage amplification efficiency (PE), we refer the amplification efficiency (E) to PCR product increase (1 to 2) in this article. PCR amplification efficiency can be either defined as percentage (from 0 to 1) or as time of PCR product increase per cycle (from 1 to 2). Typically several replicates are used for each diluted concentration to derive amplification efficiency. For each sample, a target gene and a reference gene for internal control are included for PCR amplification from serially diluted aliquots. The experiment will involve a control sample and a treatment sample. The experimental systems for both models are similar. Two mathematical models are very widely applied: the efficiency calibrated model and the ΔΔCt model. Since relative quantification is the goal for most for real-time PCR experiments, several data analysis procedures have been developed. Relative quantification relies on the comparison between expression of a target gene versus a reference gene and the expression of same gene in target sample versus reference samples. Absolute quantification is important in case that the exact transcript copy number needs to be determined, however, relative quantification is sufficient for most physiological and pathological studies. Absolute quantification employs an internal or external calibration curve to derive the input template copy number. Real-time PCR data are quantified absolutely and relatively. The cycle number at the threshold level of log-based fluorescence is defined as Ct number, which is the observed value in most real-time PCR experiments, and therefore the primary statistical metric of interest. A baseline and a threshold can then be set for further analysis. As shown in Figure ( (1B 1B and and1C), 1C), the plot of logarithm 2-based transformed fluorescence signal versus cycle number will yield a linear range at which logarithm of fluorescence signal correlates with the original template amount. The basis of real-time PCR is a direct positive association between a dye with the number of amplicons.
The dynamics of PCR are typically observed through DNA binding dyes like SYBR green or DNA hybridization probes such as molecular beacons (Strategene) or Taqman probes (Applied Biosystems).
Real time pcr data analysis excel serial#
Panel (C) is the output of a serial dilution experiment from an ABI 7000 real-time PCR instrument.īoth genomic DNA and reverse transcribed cDNA can be used as templates for real-time PCR. (B) shows a theoretical plot of PCR cycle number against logarithm PCR product amount. Three phases can be observed for PCRs: exponential phase, linear phase and plateau phase. (A) Theoretical plot of PCR cycle number against PCR product amount is depicted. It is possible to make the PCR amplification efficiency close to 100% in the exponential phases if the PCR conditions, primer characteristics, template purity, and amplicon lengths are optimal. During the exponential phase PCR product will ideally double during each cycle if efficiency is perfect, i.e. Real-time PCR exploits the fact that the quantity of PCR products in exponential phase is in proportion to the quantity of initial template under ideal conditions. The PCR will eventually reach the plateau phase during later cycles and the amount of product will not change because some reagents become depleted. The linear phase is characterized by a linear increase in product as PCR reagents become limited. The exponential phase is the earliest segment in the PCR, in which product increases exponentially since the reagents are not limited. A PCR has three phases, exponential phase, linear phase and plateau phase as shown in Figure Figure1. It has been broadly applied to microarray verification, pathogen quantification, cancer quantification, transgenic copy number determination and drug therapy studies. Real-time PCR is one of the most sensitive and reliably quantitative methods for gene expression analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
